- Aug 16, 2018
- 905
- 473
- 0
When considering injectable steroids, there are some fundamental aspects you must learn. Unfortunately, many individuals who decide to begin using anabolic steroids, often overlook proper injection techniques. As a result, this jeopardizes the user's health and safety in many ways. For instance, poor injection techniques can lead to abscess, infection, nerve damage, and many other serious consequences. In fact, we have all heard the horror stories on what can go wrong with intramuscular injections, so lets go over the steps we need to follow for a safe intramuscular injection.
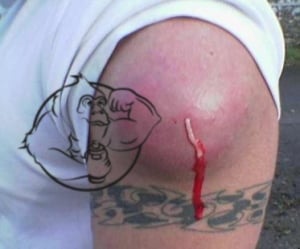
Deltoid Abscess
Sterilization
Sterilization is the most important aspect of any injection. Remember - you are about to inject a foreign substance into your body, and there can be no room for error. Therefore, any and all materials should be 100% sterile.
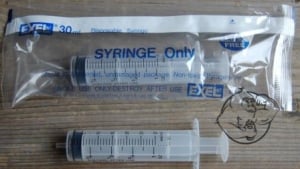
Single Use Syringes
Alcohol Wipes
Don't touch needle
Use of the proper needle
An intramuscular injection is just that - in the muscle. However, many individuals fail to use a needle appropriate for the site they are injecting in. Using a needle that is too short prevents the oil from reaching the muscle tissue. This leads to the oil being trapped within the subcutaneous layer, right before the muscle tissue, and when the oil does not reach the muscle tissue, the body does not absorb it efficiently. The trapped oil can cause abscess and infection, accompanied by severe discomfort and bruising in the injection site.

Different size needles
In the opposite situation, using a needle that is too long and going to deep can puncture vital structures of the human body such as nerves, arteries, lymphatic ducts and many other things you should never want to pierce or inject in.
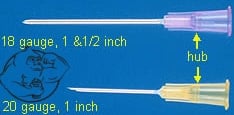
1 inch vs 1.5 inch Needle
Injecting the proper amount of oil
The muscle group you inject in can safely accommodate only a certain amount of oil. This amount will obviously vary from person to person, depending on muscle mass and experience. It is safe to say that anyone starting out should limit injections to one cc at a time.
Pre-injection techniques
There are several things one can do before injecting, which can make the experience more pleasant and less painful.
Aspirate
Neglecting this step can quickly put you in the hospital, or even worse. Once the needle has entered the muscle and you are ready to inject, you must first pull gently back on the plunger as if you were drawing in liquid, and wait approximately five seconds. This will identify any potential blood lines you may have hit. If you do not see blood enter the needle, you are good to inject the oil from the syringe. However, if blood enters the needle, you must withdraw the needle completely and start over, as this means that you have entered a bloodline. This step can not be overlooked because injecting anabolic steroids directly into the bloodstream can cause death.
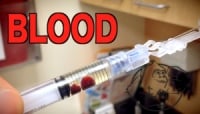
Aspirate - check for blood
In the event you aspirate and see nothing, yet halfway through the injection you feel a sharp burning, taste a funny taste or begin to cough, you must withdraw the needle. Chances are you went through bloodline initially and the injected oil is beginning to seep in.
Injecting
If the aspiration went well, you may proceed slowly and carefully to begin the act of injecting. Do not force the plunger of the syringe down - injections should be slow and steady. Once you have cleared the syringe of fluid, pause for a brief moment and then slowly withdraw the needle. After the needle has been removed from the injection site, immediately apply pressure on the injection area with an alcohol swab, or sterilized cotton pad.
Post injection
When the injection is complete and any bleeding or seepage has been stopped, it is acceptable to gently massage the injection area. This will help disperse the oil into the muscle. What's more, some individuals may also find it useful to apply a heating pad to the injection area for a short period of time. Due to the nature of certain compounds being injected in the muscle tissue, gentle massaging and applied heat can alleviate soreness and swelling as the compound settles in the muscle tissue.
In the event you withdraw the needle and experience excessive bleeding from the injection site, do not panic. Immediately apply a sterile alcohol swab or cotton pad, and apply pressure to the site.
Conclusion
With this basic introduction to intramuscular injections, you now have the necessary knowledge so safely administer your injection. There are several injection sites to choose from, many of which depend on the volume of fluid being injected. Several injection methods also exist, and can be used as one becomes more experienced in intramuscular injection. Meanwhile, inexperienced individuals should begin with the basic injection guide listed above to ensure a safe and efficient intramuscular injection.

Deltoid Abscess
Sterilization
Sterilization is the most important aspect of any injection. Remember - you are about to inject a foreign substance into your body, and there can be no room for error. Therefore, any and all materials should be 100% sterile.
- Needles and syringes are single use only! They should always be properly sealed in packaging, with no evidence of prior usage. All vials should be fully sterilized with an alcohol swab prior to use.

Single Use Syringes
- Injection sites should also be swabbed with rubbing alcohol to sterilize the area.

Alcohol Wipes
- Never touch the needle tip with your hands or fingers.

Don't touch needle
- It is a good practice to use separate needles for drawing and injecting the substance, as this ensures a sharp and sterile tip.
Use of the proper needle
An intramuscular injection is just that - in the muscle. However, many individuals fail to use a needle appropriate for the site they are injecting in. Using a needle that is too short prevents the oil from reaching the muscle tissue. This leads to the oil being trapped within the subcutaneous layer, right before the muscle tissue, and when the oil does not reach the muscle tissue, the body does not absorb it efficiently. The trapped oil can cause abscess and infection, accompanied by severe discomfort and bruising in the injection site.

Different size needles
In the opposite situation, using a needle that is too long and going to deep can puncture vital structures of the human body such as nerves, arteries, lymphatic ducts and many other things you should never want to pierce or inject in.

1 inch vs 1.5 inch Needle
Injecting the proper amount of oil
The muscle group you inject in can safely accommodate only a certain amount of oil. This amount will obviously vary from person to person, depending on muscle mass and experience. It is safe to say that anyone starting out should limit injections to one cc at a time.
Pre-injection techniques
There are several things one can do before injecting, which can make the experience more pleasant and less painful.
- Taking a warm shower before injecting. For some, this relaxes the body and relieves tension in the muscle.
- Warm the vial slightly above room temperature by rolling it in your palms for 5-10 minutes.
- Massage the injection site before injecting.
- Any air bubbles remaining in the syringe should be ejected before administering the injection.
- Intramuscular injections should be done at a 90° angle to ensure the needle reaches the muscle, and to reduce pain.
- Needles should not be “darted” into the body.
Aspirate
Neglecting this step can quickly put you in the hospital, or even worse. Once the needle has entered the muscle and you are ready to inject, you must first pull gently back on the plunger as if you were drawing in liquid, and wait approximately five seconds. This will identify any potential blood lines you may have hit. If you do not see blood enter the needle, you are good to inject the oil from the syringe. However, if blood enters the needle, you must withdraw the needle completely and start over, as this means that you have entered a bloodline. This step can not be overlooked because injecting anabolic steroids directly into the bloodstream can cause death.

Aspirate - check for blood
In the event you aspirate and see nothing, yet halfway through the injection you feel a sharp burning, taste a funny taste or begin to cough, you must withdraw the needle. Chances are you went through bloodline initially and the injected oil is beginning to seep in.
Injecting
If the aspiration went well, you may proceed slowly and carefully to begin the act of injecting. Do not force the plunger of the syringe down - injections should be slow and steady. Once you have cleared the syringe of fluid, pause for a brief moment and then slowly withdraw the needle. After the needle has been removed from the injection site, immediately apply pressure on the injection area with an alcohol swab, or sterilized cotton pad.
Post injection
When the injection is complete and any bleeding or seepage has been stopped, it is acceptable to gently massage the injection area. This will help disperse the oil into the muscle. What's more, some individuals may also find it useful to apply a heating pad to the injection area for a short period of time. Due to the nature of certain compounds being injected in the muscle tissue, gentle massaging and applied heat can alleviate soreness and swelling as the compound settles in the muscle tissue.
In the event you withdraw the needle and experience excessive bleeding from the injection site, do not panic. Immediately apply a sterile alcohol swab or cotton pad, and apply pressure to the site.
Conclusion
With this basic introduction to intramuscular injections, you now have the necessary knowledge so safely administer your injection. There are several injection sites to choose from, many of which depend on the volume of fluid being injected. Several injection methods also exist, and can be used as one becomes more experienced in intramuscular injection. Meanwhile, inexperienced individuals should begin with the basic injection guide listed above to ensure a safe and efficient intramuscular injection.

