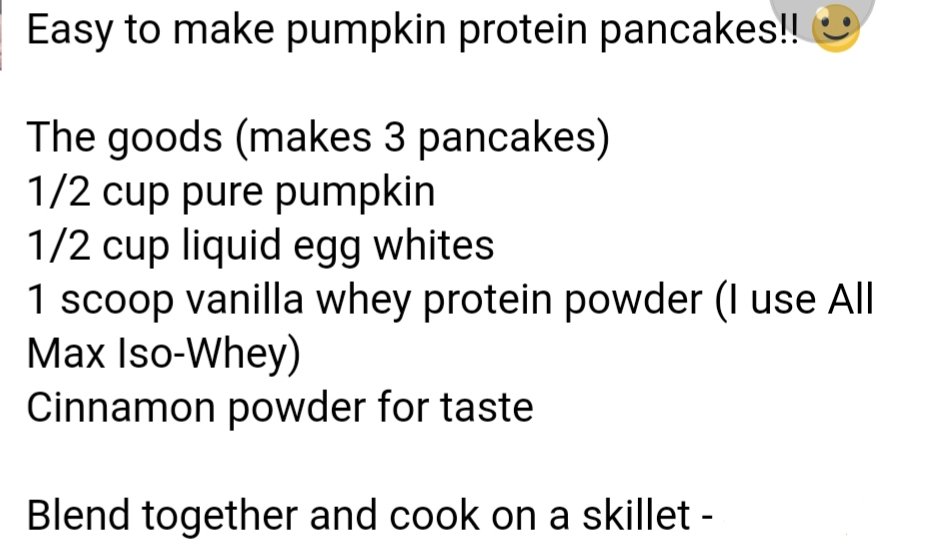-
Posts
912 -
Joined
-
Last visited
-
Days Won
71
Everything posted by musclebeauty
-

Pre and post workout snacks
topic replied to musclebeauty's musclebeauty in Nutrition, Diet and Recipes
Thanks hun? -
PRE- AND POST-WORKOUT SNACKS Personal trainers constantly hear the refrain: “I just never know what to eat before a workout!” Questions about what to eat to optimize a workout are not uncommon, and may be of critical importance to the success of your fitness goals. Your body has very particular needs that depend on your age, sex, fitness level, and training goals. It may take some trial and error to find the best meals to fit your pre- and post-workout needs but practice makes perfect and we’re certain this information will help you identify the perfect portions for you. What Should I Look for on the Nutrition Labels of My Pre- and Post-Workout Snacks? The United States Department of Agriculture [USDA] (2016) explains that our bodies require three different types of macronutrients: carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. Carbohydrates come in the form of sugars, starches, and fibers, which differ in their complexity and molecular length. In general, however, carbohydrates can be broken down into glucose molecules, which the body relies on as its primary source of energy. Fats are another building block of nutrition. Although fats have gotten a bad rap, they are an important source of energy for the body. During a workout, the body will quickly use up all of the available glucose created from the digestion of carbohydrates. If carbs aren’t readily available, the body can break into its stores of fat to get the energy it needs (USDA 2016). Finally, proteins are made up of chains of molecular building blocks called amino acids. These amino acids can be used to build parts of cells, create enzymes, or help cells signal to one another. Your body only uses proteins for fuel if carbohydrates and fats are unavailable. Each gram of fat contains 9 calories, while each gram of carbohydrates or proteins contains just 4 calories. If you are trying to lose weight, it is necessary to burn more calories than you take in each day. Thus, you must be mindful of your patterns of consumption when it comes to balancing your intake of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins (USDA 2016). Clarify Your Training Goals to Inform Your Nutritional Needs There is no single answer to the question, “What is the perfect pre-workout food?” The answer depends completely on your training goals; for example, an Olympic powerlifter needs a much different post-workout snack than someone simply trying to lose some weight. When determining your nutritional needs, think about your overall training goals. Are you hoping to lose weight and eliminate excess body fat, focusing on building your endurance for a long race, or engaging in frequent weight lifting to build muscle mass? Each of these goals will result in vastly different nutritional needs. Pre-Workout Nutrition Requirements The American Heart Association (2015) advises that before your workout, you should provide your body with nutrients that it can easily convert into energy. This typically means carbohydrates. Approximately two hours before you hit the gym, eat one or two servings of complex carbohydrates. A good pre-workout meal may include whole-wheat toast, low-fat yogurt, brown rice, or whole-grain cereals. Two hours gives your body time to digest these complex carbohydrates into easy-to-use glucose molecules. If you’re running short on time, choose a pre-workout snack that is an easily digestible source of carbohydrates. A piece of fruit typically does the trick, offering a natural and fibrous source of simple sugars. Wash it down with a full glass of water to start your workout with proper hydration. Do You Need to Eat During a Workout? Some athletes fuel their bodies during a workout, while others opt not to do so. Again, the optimal decision depends on your training goals. According to the American Heart Association (2015), there is no need to fuel mid-workout if you’re exercising for less than 60 minutes. The same rule applies to weight lifting exercises designed to increase muscle mass. For these sessions, your pre workout snack will suffice to provide energy, while post workout nutrition becomes more critical. For people training for aerobic endurance, it is a smart idea to give your body a small amount of fuel if you are training for longer than one hour. When engaging in longer workouts at a high intensity, eat 50 to 100 calories each half hour. This might include some raisins or dried fruit, a banana, or a small energy bar. Even more important than food is ensuring that your body gets enough fluid during a workout. Drink water frequently during aerobic exercise, taking small sips every few minutes. This ensures that your tissues will work properly during and after your workout. For longer workouts, consider grabbing an energy drink or a gel fuel pouch to replace the electrolytes you are losing through sweat. Post-Workout Nutrition for Recovery After you finish your workout, your body enters recovery mode. This means that your tissues begin to rebuild and replenish themselves. Many athletes wonder what to eat after a workout to facilitate this recovery process. In fact, creating the perfect post-workout snack is critical to reaching your goal, whether it entails losing weight, boosting endurance, or building muscle mass. Your body has two major nutritional needs during recovery: carbohydrates and proteins. In the 20 to 60 minutes following your workout, carbohydrates provide much-needed energy to muscle fibers. Proteins, on the other hand, are essential building blocks to repair muscle tissue that is torn during a workout. This tissue rebuilding process goes on for several hours following a workout, but your body benefits most if you consume protein within 30 minutes of ending your exercise routine (American Heart Association, 2015). The relative ratio of carbohydrates to proteins depends on your training goals. If you are focusing on aerobic exercise to build cardiovascular endurance, a 1:1 ratio of proteins to carbohydrates is fine. If your goal is to build muscle mass, you will want a snack that is closer to a 2:1 ratio of proteins to carbohydrates. The extra protein is needed to provide you with the amino acids necessary to create muscle tissue. Keep focused on the calories in your post-workout nutrition, particularly if you are trying to lose weight. Many energy bars are high in sugar and calories, which can be detrimental to your fitness goals. Instead, make yourself a shake using protein powder, which also rehydrates your body. Alternatively, eat a banana with peanut butter, tuna on whole wheat bread, hummus with whole wheat pita bread, or a snack mix with nuts and dried fruits (Whitmore, 2001). References American Heart Association. (2016, January 08). Food as Fuel - Before, During and After Workouts. Retrieved February, 2016, from https://www.heart.org/HEARTORG/HealthyLiving/PhysicalActivity/FitnessBasics/Food-as-Fuel---Before-During-and-After-Workouts_UCM_436451_Article.jsp United States Department of Agriculture. (2016, January 29). Macronutrients. Retrieved February, 2016, from https://fnic.nal.usda.gov/food-composition/macronutrients Whitmore, L. K. (n.d.). 6 Smart Snacks for After Your Workout. Retrieved February 25, 2016, from http://www.fitnessmagazine.com/recipes/snacks/low-calorie/after-workout-snacks/
-

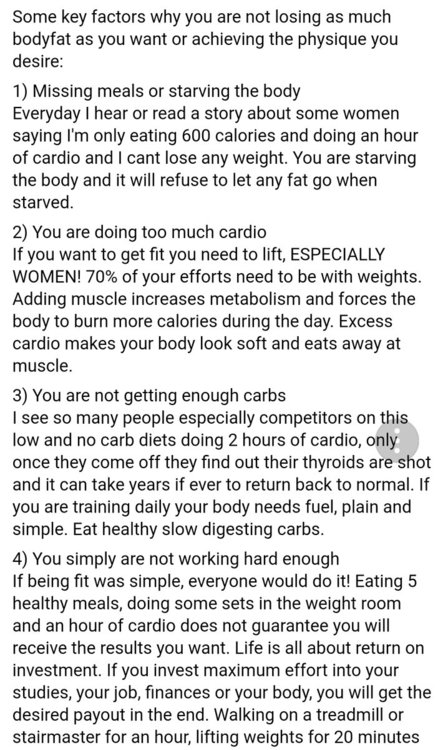
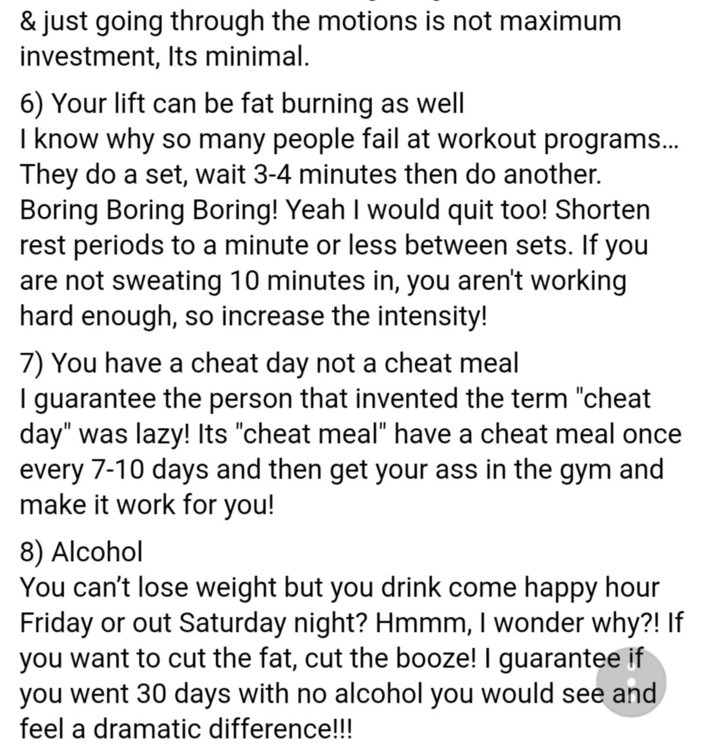
Why am i not losing much bodyfat?
topic replied to musclebeauty's musclebeauty in Bodybuilding and Training Talk
Im glad if this info can help -
I appreciate the info hun i think i will go up to 400mg see how my tolerance is with that in the next 2 days...i think your right that may be my sweet spot. Im still doing cardio but limited compared to what i was doing making sure to drink tons of water and stay cool.....
-
LGD-4033, known also as Ligandrol and Anabolicum, is the strongest orally bioavailable, non-steroidal, selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM) currently on the market. Popular with athletes, power lifters and body builders for its ability to both bulk and cut, Ligandrol produces steroid-like results without the side effects. It’s considered an excellent supplement for those looking to recomp: reduce their body fat and increase lean muscle mass. From a medical perspective, Ligandrol is being studied to treat conditions such as muscle wasting linked with acute and chronic diseases, age-related muscle loss, Osteoporosis and cancer. Let’s take a closer look… History Behind LGD 4033 LGD-4033 was originally discovered by Ligand pharmaceuticals and is currently under development by Viking Therapeutics as VK5211. From the start, LGD-4033 has been anticipated to yield the healing benefits of testosterone with better safety, admissibility and patient acceptance due to tissue-selective mechanism of action and its oral form of administering. How it Works Ligandrol works in the same way as other SARM’s: by selectively activating androgen receptors to promote anabolic activity exclusively in muscle and bone. Studies show [1] that LGD-4033 has a high affinity muscle and bone AR’s rather than prostate, liver or sebaceous glands, which makes it an ideal SARM for building and preserving muscle mass and bone mineral density. Why YOU Should Take Ligandrol: The Benefits There are 7 primary benefits that have been observed in both initial studies and user-reported reviews of LGD-4033… LGD-4033 increases lean muscle mass. The clear-cut primary benefit of supplementing with Anabolicum is its ability to increase lean muscle mass without increasing fat when bulking.The Phase 1 trial showed that participants taking 1.0mg of Ligandrol gained on average 2.66lbs (1.21kg) of lean body mass over the 21-day period. This increase was dose-dependent, meaning the more LGD-4033 taken, the more lean muscle mass was created. [1]NB:Recommended dosage is 10mg per day. We do not advocate going higher than this dose. LGD-4033 may improve strength and stamina. One key study measured participants stair-climbing speed and power as an indicator of muscle strength and endurance. Results from the 21-day study indicated a trend towards dose-related improvement of stair-climbing speed and power thanks to LGD. [1]Real users have noted an increase in muscle strength and stamina while cycling Ligandrol, which correlates with the increase in lean muscle mass seen in studies. LGD-4033 selectively targets muscle and bone tissue. As a true SARM, LGD targets the AR almost exclusively in muscle and bone tissue, which is why it is being studied to prevent and treat caxechia, sarcopenia, osteoporosis and older individuals recovering from hip fractures.Studies show that, even though there was clear androgenic activity in muscle and bone tissue, the prostate-specific antigen did not change significantly when taking the correct Anabolicum dosage. LGD-4033 may increase fat loss. LGD has amazing anti-catabolic activity, which means it prevents the breakdown of hard earned muscle. This is why lean body mass has been reported in some users to increase even during a caloric deficit.Ligandrol also indirectly reduces body fat by increasing muscle and bone cells, which are more metabolically expensive to maintain than fat cells. By increasing muscle mass, an increase in the catabolic activity metabolism is seen, which results in easier fat loss.https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3661116/Many users report stacking LGD-4033 with S4 (Andarine) to support simultaneous bulking and cutting. LGD-4033 boosts mental well-being. Many users have reported feeling positive, strong and a sense of ‘alpha’ when taking Ligandrol. This state of mental wellbeing and what some have called a slight feeling of ‘aggression’ benefits their lifts in the gym as it improves their competitive streak. Just be sure not to get too competitive and keep your lifts smart and safe. LGD-4033 may help patients recover from hip fractures. Phase 2 of the clinical trial of Ligandrol is currently underway. Viking Pharmaceuticals noticed that older individuals are at higher risk of suffering a hip fracture and, due to sarcopenia (the natural decline of muscle mass after the age of 30), it’s harder for individuals to both retain and build lean muscle mass.Combined with a hip fracture, and the rate of morbidity due to complications after a fall increases.A supplement such as Ligandrol, which helps increase bone mineral density as well as increase lean muscle mass without the side effects of traditional treatments such as steroids is a promising treatment for an otherwise overlooked population. LGD-4033 may treat muscle wasting caused by cancer. Anabolicum’s Phase 1 clinical trial showed promising results for building and preserving lean muscle mass in healthy young men, which has lead Viking Pharmaceuticals to investigate how LGD could be used to treat caxechia (muscle wastage) caused by cancer. Trials are currently underway (2016). [2] The Side Effects of LGD 4033 As with all supplements, some side effects have been noted by both users of Ligandrol and during studies. However, it’s worth noting that side effects of LGD-4033 appear to be not only minimal and reversible, but outweighed by the benefits. The primary Clinical Trial Phase 1 showed that LGD-4033 was well-tolerated and safe at all doses. However, some side effects reported by users online include: Headaches Hair growth as well as shedding Nausea Fatigue Muscle Pumps However, whether these side effects can be attributed to Ligandrol is hard to say, as some users do not purchase their SARMs from reputable sources. Keep in mind that results and side effects vary by individual, particularly as a minimally-studied, non-FDA approved supplement. Bottom Line: There have been no serious or long lasting negative effects reported as a result of taking LGD 4033. And with it’s 24 hour half life, anything you DO experience will go away pretty quickly. I also recommend you limit each cycle to a maximum of 6 weeks and take a full month off before you take it again. Don’t be stupid, or irresponsible, and always be aware of how your body is responding to it and you’ll be okay. Does LGD-4033 cause temporary suppression of testosterone? An interesting side effect of Ligandrol is a dose-dependent suppression of total testosterone and hormone-binding globulin levels. Although Ligandrol increased lean body mass, the study showed testosterone suppression from baseline to day 21 of the three-week study. [1] However, once LGD-4033 was discontinued, testosterone levels returned to their normal baseline by day 56. A mini-PCT (Post Cycle Therapy) should assist the body in returning to baseline. Dosing Guidelines Benefits have been documented with dosages as little as 3-10mg every 24 to 36 hrs. Research subjects have been know to tolerate therapy with notable benefits after 2 weeks with improvements continuing for up to 5 months (20 weeks). Note that research recognizes a increase in tolerance after 3 months with benefits continuing to decrease. Many male users report the upper ideal limit for LGD to be 10mg per day in the morning for twelve weeks. Although some women have reported using LGD-4033, it has been suggested that it may cause masculinisation lower doses are recommended. Females are advised to stick to an upper limit of 5mg per day. The chart below is a simple guideline that will work for 99.9% of people: LGD 4033 Dosing Guidelines For Bulking: A protein-rich diet is also necessary as well as higher caloric intake if you plan to beef up by at least 10 lbs. For Cutting: Use LGD-4033 with SARMS triple pack (GW-501516, S-4 and LGD-4033) to make it more effective as you are aiming to add more size while cutting fat. Suggested dosage is 3-5 mg a day for 8 weeks. For Recomping: LGD-4033 is best used for recomping. Many users have said that they’ve observed a boost in lean body mass and fat loss. Using it together with other SARMS such as GW-501516 or Cardarine will give you a stronger and better recomp. Suggested dosage is 5-8 mg per day for 8 weeks. In the studies done on Ligandrol they are using sometimes as little as 1mg and still seeing pronounced muscle gain. This randomized, double-blind study showed that it was safe even up to 22 mg per day for average people. Post Cycle Therapy (PCT) Post Cycle Therapy (PCT) is required when taking SARMS to help preserve muscle gains, prevent fat accumulation, maintain mood and motivation, and retain strength in muscles. Cycling also helps to allow hormone levels to return to their natural state in order to prevent unwanted dependency. Typically, a PCT will last the same duration as supplementation. So if a user supplemented with a hormone for 12 weeks, a PCT of 12 weeks would also be required to bring their hormones back to baseline. But do I need a PCT when taking SARMs? Typically, SARMs do not disrupt hormone levels in the body, which means that a traditional PCT is not necessary. However, studies and user reviews show that LGD-4033 temporarily decreases testosterone levels. These levels are quickly reversed when supplementation is stopped, and a mini PCT can help speed up the recovery process.
-
Ok on day 6 of BT's DNP and feeling actually fine get a little hotter at night time and sweat more when i train but nothing extreme. I bumped my dose upto 300mg since i cap my own pills now. Trying to limit carb intake just to avoid the extreme heat you can get from the DNP.. so far so good and dropping weight...
-
Welcome Dngerfield i hope you enjoy the board and glad to have you...
-
Just a very interesting article i found hope you enjoy.... Unlike weight training, which involves lifting weight to improve general health and lean muscle mass, bodybuilding is specifically geared toward massive muscle growth with an emphasis on appearance over performance. This emphasis requires athletes in the sport of bodybuilding to retain a lean body that puts the definition of their muscles on display. To this effect, their diet must facilitate fat metabolism. Well, hold on, this means that bodybuilding requires pursuing two contrary goals simultaneously: both increasing and decreasing body mass. In order to accomplish both goals, training is usually parsed into two phases: bulking and cutting. But wait one minute- we all know the feeling of getting stuck in a bulking rut. It's tough to lose fat, and mass doesn't just magically convert to lean muscle. Well, if you find the strict dichotomy of bulk and cut to be a bit suspicious then you're headed in the right direction. Replacing "Bulk & Cut" with a Solution that Works A healthy bodybuilding diet is more nuanced than simply alternating between periods of caloric surplus and caloric defecit. Instead, bodybuilders should focus on utilizing intermittent fasting and specialized nutrition to attain their goals. Right now, you're probably scratching your head wondering how fasting can help you build a muscular physique. Well, I know what you're thinking- doesn't skipping a meal cause your body to cling to your calories as fat? Won't fasting make it harder to build muscle and more difficult to lose fat? Think again. Most anyone who has tried to build muscle knows that your muscles require rest between workouts. While some opt to rotate muscle groups, others take a day between weight lifting sessions to work on cardio and core workouts. We recommend the latter. The reason? Taking designated periods of "rest" allows your body to get in a rhythm that supports the aims of bodybuilding. Fasting during these periods of cardiovascular workouts trains the body to rely on its fat stores for energy. In fact, studies show that fasting on alternating days leads to weight loss in non-obese subjects. What's more is that this weight loss corresponds with increased fat oxidation and reduced fat mass in the body (Heilbronn, Smith, Martin, Anton & Ravussin, 2005). But, How Do Bodybuilders Build Muscle With Fewer Calories? The short answer is: they don't. As stated, bodybuilders need to utilize intermittent fasting and specialized nutrition. On days focused on building muscle, it's essential to provide your body with the proper fuel, which means consuming more calories than the body burns (Lambert, 2004). During most of bodybuilding training, the overriding goal is to stimulate muscle growth. There are two components of muscle growth: stimulation and repair, both of which can be supported and enhanced by the proper diet. Stimulation occurs while training at the gym; repeatedly contracting muscles while under a significant weight load causes muscle fibers to become damaged. During the repair phase, tissue undergoes healing that eventually causes muscle hypertrophy, or growth (Schoenfeld, 2010). Muscle repair depends on the availability of amino acids, which are the building blocks of protein. When you eat protein, your body breaks it down into its components, amino acids. These amino acids are rearranged and built into new proteins that make muscle tissue larger. As a result, protein is the number one concern for bodybuilders looking to increase muscle mass. The specific guidelines for a bodybuilding diet include 55 to 60% of calories from carbohydrates, 25 to 30% from protein, and 15 to 20% from fat (Lambert, 2004). Keep in mind that because fats contain more calories, a relatively smaller amount of high-fat foods are needed to achieve this balance. This diet should remain consistent throughout training with days of intermittent fasting keeping diet composition consistent while reducing caloric intake. In other words, on rest days, eat the same food- but less of it. So, Which Foods Are Best Included in a Successful Bodybuilding Diet? The Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics recommends that bodybuilders eat 1.2 to 1.7 grams of protein per kilogram bodyweight each day (Caspero, 2014). For example, a 190-pound (86 kg) bodybuilder should aim for 103 to 147 grams of protein daily. Lean protein is best, as it contains relatively less saturated fat. Consider the following protein sources for a healthy bodybuilding diet (Utah State University Extension): Chicken breasts (skinless) Ground beef Ground turkey Yellowfin tuna Halibut Salmon Canned tuna Cottage cheese Greek yogurt Sardines Navy beans Mixed nuts Lentils Peanut butter In addition to lean protein, carbohydrates form a critical component of the bodybuilding diet. Carbohydrates are particularly useful immediately following a workout (Helms et al., 2014). This is because during an anaerobic weight training session, the body uses up stores of glycogen to fuel the workout. Eating carbohydrates following a workout replaces this storage form of glucose, aiding recovery. Effective forms of carbohydrates include fruits, oatmeal, pasta, sweet potatoes, corn, peas, or whole-wheat bread. An effective bodybuilding diet typically involves at least five or six small, nutrient-dense meals throughout the day (Helms et al., 2014). This helps to keep energy levels high and allows the body to have enough nutrients to repair damaged muscle tissue. To fast effectively, we recommend eating your last meal a few hours before bed and skipping the first meal of the day until your cardio workout is completed. Remember, for fasting to be an effective strategy, this meal cannotbe substituted with more meals or larger portions later in the day. Wait! Stay Safe When Building Muscle By Ensuring the Nutritional Adequacy of Meals Although a bodybuilding diet can be healthy, many athletes focus on muscle growth to the exclusion of other health factors. Several research studies have found that competitive bodybuilders have nutrient deficiencies, poor hydration, and signs of physiological stressors (Kleiner et al., 1990; Too et al., 1998). You can't compete if you're not well, and it's never okay to sacrifice your health for your appearance. So, no matter your goals, remember that focusing on dietary needs specific to bodybuilding does not overshadow the importance of a healthy and overall well-balanced diet. References Caspero, A. (2014). Protein and the athlete: how much do you need? Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics. Retrieved from http://www.eatright.org/resource/fitness/sports-and-performance/fueling-your-workout/protein-and-the-athlete Heilbronn, L. K., Smith, S. R., Martin, C. K., Anton, S. D., & Ravussin, E. (2005, January). Alternate-day fasting in nonobese subjects: Effects on body weight, body composition, and energy metabolism. Retrieved September 08, 2016, from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15640462
-

Why am i not losing much bodyfat?
topic replied to musclebeauty's musclebeauty in Bodybuilding and Training Talk
Thankyou very much hun... -

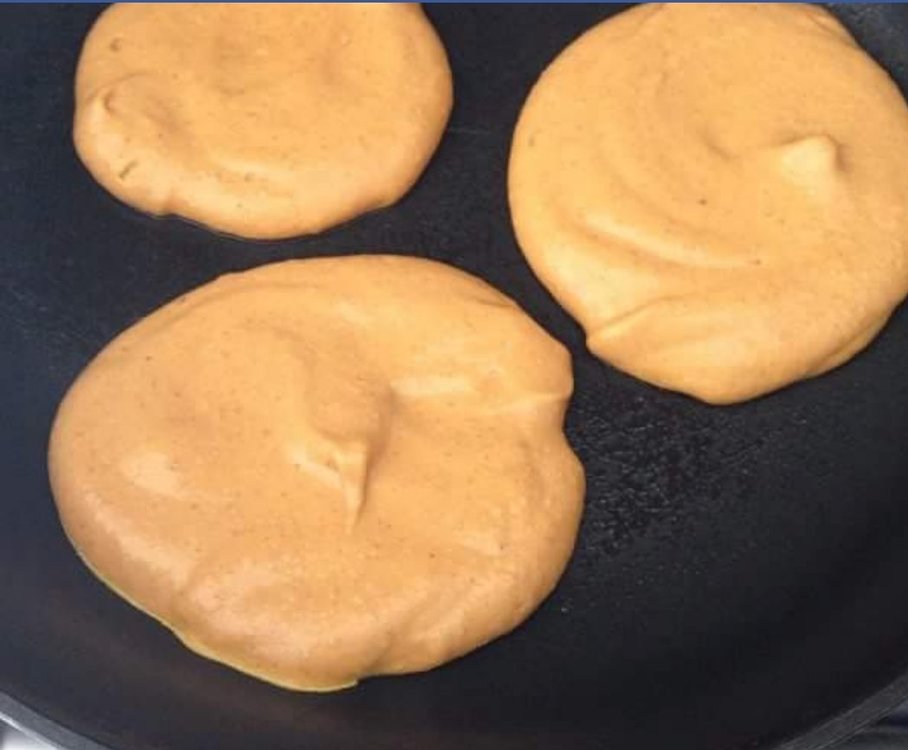
Simple and easy to make protein pancakes
topic replied to musclebeauty's musclebeauty in Nutrition, Diet and Recipes
You can just throw them in -
-
-

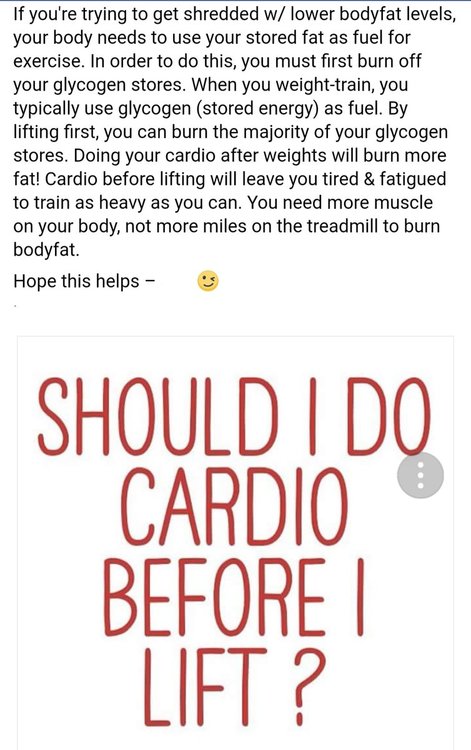
Should you do cardio before you lift?
topic replied to musclebeauty's musclebeauty in Bodybuilding and Training Talk
Yes i do cardio after training as well i used to do it before when i started bodybuilding but found out i had no energy left to train... -
-

Can A Massage Help In Muscle Recovery
topic replied to musclebeauty's musclebeauty in Bodybuilding and Training Talk
Too funny lol -

Buying Supplements on a Budget
topic replied to musclebeauty's musclebeauty in Bodybuilding and Training Talk
No problem hun -
Now i dont know about you but i love reese peanut butter cups so i came up with this little mix sooooo good....